RIVETS AND RIVETED JOINTS
Riveted
joints:
In riveted joints were classified
as one of the types of permanent fastenings. They are generally used to fasten
metal plates and steel section in structural works such as bridge and roof
trusses and in the construction of pressure vessels such as storage tanks
boilers. The field of application of riveted joints has been considerably
reduced by the welded joints because of the simplified process of making the
welded joint comparative strength and economy. However riveted joints are very
effective in designs subjected to pronounced vibration loads where welded
joints are less reliable. Riveted joints may also be employed to connect metals
which are difficult to weld together and in the joints which permit no heating welded
due to possible tempering or warping of the finished machine parts.
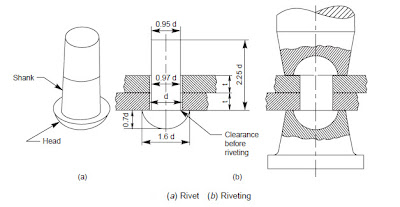
Rivet:
A rivet is a round rod of either mild steel or nonferrous
materials such as copper aluminum with a head of any one of the shapes formed
at one end during its manufacture and its tail end being slightly tapered as
the length of the shank of the rivet should accommodate the thickness of the
connecting plates and also provide sufficient material for forming the head at
the tail end in general the eight of shank of the rivet will be equal to sum of
the thickness of the connecting plates plus 105 to times the diameter of the rivet.
If
l = length of the shank of the rivet
d
= diameter of rivet
r
= thickness each of the connecting plates then
l
= ∑t + (1.5 to 1.7) d
Riveting:
Riveting is the process of forming a well shaped
concentric head from the project-ting tail end of the shank rivets inserted in
the holes previously drilled in the plates to be fastened, without allowing it
to develop an initial stress so that it can take up the designed working shear load.
The process of making the riveted joint involves making of the hole in the
plates and the formation of the head out of the projecting tail end of the
shank of the rivet.
Riveted joints must be made air tight in applications such as boilers and other pressure vessels.Caulking or fullering is done to make the riveted joints air tight.
Caulking:
The outer edges of the plates used in boiler and other pressure vessels are beveled To produce air tight riveted joints, these beveled edges of the plates are caulked. Caulking is an operation in which the outer bevel led edges of the plates are hammered and driven-in by a caulking tool.The caulking tool is in the form of a blunt edged chisel.
Fullering:
Similar to caulking, fullering is also used to produce air tight joints. Unlike the caulking tool, the width of the fullering tool is equal to the width of the beveled edges of the plates Caulking and fullering operations are carried out effectively by applying pneumatic pressure.
Lap Joint:
In a lap joint, the plates to be riveted, overlap each other. The plates to be joined are first beveled at the edges, to an angle of about 80° . Depending upon the number of rows of rivets used in the joint, lap joints are further classified as single riveted lap joint.
Butt Joint:
In a butt joint, the plates to be joined, butt against each other, with a cover plate or strap, either on one or both sides of the plates; the latter one being preferred. In this joint, the butting edges of the plates to be joined are square and the outer edges of the cover plate(s) is(are) beveled In a single strap butt joint, the thickness of the strap (cover plate) is given by, t1 = 1.125t If two straps are used, the thickness of each cover plate is given by, t2 = 0.75t.
Emperical
proportions of Rivet joints:
For
the given thickness of the connecting plates the other dimensions such as rivet
diameter pitch the distance from the centre of the rivet to the edge of the
plate transverse pitch thickness of the cover plates in case of butt joints that
are required to make the riveted joints are obtained from the Emperical
proportions. For general use the Emperical proportions given in the may be
used. In the design of the boiler joints the Emperical proportions specified by
the Indian boiler regulations.
Emperical
proportions for general use:
The
following Emperical proportions may be used for riveted joints in general class
of work.
Diameter
of rivet: d = 6√ t mm
Where t = thickness of the
connecting plates in mm
Longitudinal
pitch: p =3d
Center
of the rivet to the edge of the plates = 1.5 d
Transverse
pitch: pt = 0.6 p…. For zig-zag riveting
Pt = 0.8 p…. For chain riveting
Thickness
of cover plates or butt straps:
Thickness of single cover
plate t₁ = 1.125 t
Thickness of double cover
plate t₂ = 0.7 t to 0.8 t.
Emperical
proportions for Boiler joints:
In the design of riveted joints for boiler work the
following Emperical proportions as specified by the Indian boiler regulation
known as I.B.R. should be used.
Lap joints:
Diameter of rivet: d = 6√ t mm
Where t = thickness of
the connecting plates in mm
Longitudinal pitch p:
p = 2t + 4lmm ….. For single riveted
p = 2t + 4lmm ….. For double riveted
p = 2t + 4lmm ….. For treble riveted
p = 2t + 4lmm ….. For quadraple riveted
Center
of the rivet to the edge of the plates = 1.5 d
Transverse
pitch pt:
Pt = 2d…. For chain
riveting
Pt = 0.33 p +0.67d …. For zig-zag
riveting
Boiler joints:
Diameter of rivet: d = 6√ t mm
Where t = thickness of
the connecting plates in mm
Longitudinal pitch p:
p = 1.53t + 4lmm ….. For
single riveted and single strap
p = 3.06t + 4lmm ….. For double
riveted and single strap
p = 4.05t + 4lmm ….. For treble
riveted and single strap
p = 1.75t + 4lmm ….. For
single riveted and double strap
p = 3.5t + 4lmm ….. For double
riveted and double strap
p = 4.63t + 4lmm ….. For treble
riveted and double strap
p = 5.52t + 4lmm ….. For quadraple
riveted and double strap
Center
of the rivet to the edge of the plates = 1.5 d
Transverse
pitch pt:
Pt = 2d…. For chain
riveting
Pt = 0.33 p +0.67d …. For zig-zag
riveting
Thickness
of cover plates or butt straps:
Thickness of single cover
plate t₁ = 1.125 t
Thickness of double cover
plate t₂ = 0.625t.





I have read this blog very useful information about Rivet joints..Thanks
ReplyDeletehttp://www.ushaprecision.com/